POTELIGEO has a consistent safety profile with up to 5 years of data1
POTELIGEO has had no cumulative safety issues associated with long-term exposure1,a
- No increase in rates of infusion reaction from primary analysis
- No new safety or autoimmune concerns emerged with longer exposure
No new safety issues with exposure up to 5 years1
Primary analysis range of treatment exposure to POTELIGEO included >1 month to2:
Additional exposure during long-term safety follow-up after primary analysis1,a
48% of patients treated for at least 6 months2
23% of patients treated for at least 12 months2
Adverse reactions in ≥10% of patients with a ≥2% higher incidence within the POTELIGEO treatment arm2,3,b,c
- Adverse reactions in the crossover arm were generally consistent with those in the POTELIGEO arm
- Serious adverse reactions reported in >2% of patients randomized to POTELIGEO were pneumonia (5%), sepsis (4%), pyrexia (4%), and skin infection (3%)2
| ADVERSE REACTIONS |
POTELIGEO IV (n=184) |
Vorinostat PO (n=186) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body system | All grades (%) | ≥Grade 3 (%) | All grades (%) | ≥Grade 3 (%) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | ||||
| Rash, including drug eruption | 35 | 5 | 11 | 2 |
| Drug eruptiond | 24 | 5 | <1 | 0 |
| Procedural complications | ||||
| Infusion-related reactiond | 33 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Infections | ||||
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 22 | 0 | 16 | 1 |
| Skin infection | 19 | 3 | 13 | 4 |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||||
| Musculoskeletal pain | 22 | <1 | 17 | 3 |
| General disorders | ||||
| Pyrexia | 17 | <1 | 7 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Mucositis | 12 | 1 | 6 | 0 |
Of the 136 patients who crossed over to POTELIGEO, 20% were due to adverse reactions.4
No specific laboratory test is required to prescribe POTELIGEO.
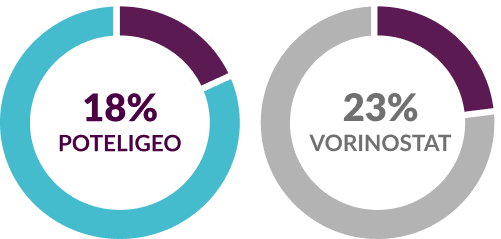
Discontinuation due to adverse reactions2,4
- aLong-term exposure was defined as >351 days of exposure to POTELIGEO.1
- bAdverse reactions include groupings of individual preferred terms.2
- cIncludes adverse reactions reported up to 90 days after randomized treatment.2
- dPer study protocol, patients taking low-/intermediate-potency topical steroids or low-dose (≤20 mg) systemic steroids for at least 4 weeks could continue. However, initiation or increase in dose while on study was not permitted unless to treat an infusion reaction (systemic) or acute rash (topical).3
- PO=by mouth
Being able to distinguish between treatment-related rash and disease progression is an
important step in managing patients
patients
- Bagot M, Dalle S, Sokol L, et al. Long-term disease control and safety with the anti-CCR4 antibody mogamulizumab: post-hoc analyses from the MAVORIC trial of patients with previously treated cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Dermatol Ther. 2022;35(8):e15634.
- POTELIGEO [package insert]. Kyowa Kirin Inc., Princeton, NJ USA.
- Kim YH, Bagot M, Pinter-Brown L, et al. Mogamulizumab versus vorinostat in previously treated cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (MAVORIC): an international, open-label, randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(9):1192-1204. Supplementary appendix published online August 9, 2018.
- Kim YH, Bagot M, Pinter-Brown L, et al. Mogamulizumab versus vorinostat in previously treated cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (MAVORIC): an international, open-label, randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19(9):1192-1204.
